MongoDB建模
MongoDB 建模
MongoDB 的数据模式是一种灵活模式,关系型数据库要求你在插入数据之前必须先定义好一个表的模式结构,而 MongoDB 的集合则并不限制 document 结构。这种灵活性让对象和数据库文档之间的映射变得很容易。即使数据记录之间有很大的变化,每个文档也可以很好的映射到各条不同的记录。 当然在实际使用中,同一个集合中的文档往往都有一个比较类似的结构。
数据模型设计中最具挑战性的是在应用程序需求,数据库引擎性能要求和数据读写模式之间做权衡考量。当设计数据模型的时候,一定要考虑应用程序对数据的使用模式(如查询,更新和处理)以及数据本身的天然结构。
MongoDB 数据建模入门
参考:https://docs.mongodb.com/guides/server/introduction/#what-you-ll-need
(一)定义数据集
当需要建立数据存储时,首先应该思考以下问题:需要存储哪些数据?这些字段之间如何关联?
这是一个数据建模的过程。目标是将业务需求抽象为逻辑模型。
假设这样一个场景:我们需要建立数据库以跟踪物料及其数量,大小,标签和等级。
如果是存储在 RDBMS,可能以下的数据表:
| name | quantity | size | status | tags | rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| journal | 25 | 14x21,cm | A | brown, lined | 9 |
| notebook | 50 | 8.5x11,in | A | college-ruled,perforated | 8 |
| paper | 100 | 8.5x11,in | D | watercolor | 10 |
| planner | 75 | 22.85x30,cm | D | 2019 | 10 |
| postcard | 45 | 10x,cm | D | double-sided,white | 2 |
(二)思考 JSON 结构
从上例中可以看出,表似乎是存储数据的好地方,但该数据集中的字段需要多个值,如果在单个列中建模,则不容易搜索或显示(对于 例如–大小和标签)。
在 SQL 数据库中,您可以通过创建关系表来解决此问题。
在 MongoDB 中,数据存储为文档(document)。 这些文档以 JSON(JavaScript 对象表示法)格式存储在 MongoDB 中。 JSON 文档支持嵌入式字段,因此相关数据和数据列表可以与文档一起存储,而不是与外部表一起存储。
JSON 格式为键/值对。 在 JSON 文档中,字段名和值用冒号分隔,字段名和值对用逗号分隔,并且字段集封装在“大括号”({})中。
如果要开始对上面的行之一进行建模,例如此行:
| name | quantity | size | status | tags | rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| notebook | 50 | 8.5x11,in | A | college-ruled,perforated | 8 |
您可以从 name 和 quantity 字段开始。 在 JSON 中,这些字段如下所示:
{ "name": "notebook", "qty": 50 }(三)确定哪些字段作为嵌入式数据
接下来,需要确定哪些字段可能需要多个值。可以考虑将这些字段作为嵌入式文档或嵌入式文档中的 列表/数组 对象。
例如,在上面的示例中,size 可能包含三个字段:
{ "h": 11, "w": 8.5, "uom": "in" }And some items have multiple ratings, so ratings might be represented as a list of documents containing the field scores:
[{ "score": 8 }, { "score": 9 }]And you might need to handle multiple tags per item. So you might store them in a list too.
["college-ruled", "perforated"]Finally, a JSON document that stores an inventory item might look like this:
{
"name": "notebook",
"qty": 50,
"rating": [{ "score": 8 }, { "score": 9 }],
"size": { "height": 11, "width": 8.5, "unit": "in" },
"status": "A",
"tags": ["college-ruled", "perforated"]
}This looks very different from the tabular data structure you started with in Step 1.
数据模型简介
数据建模中的关键挑战是平衡应用程序的需求、数据库引擎的性能以及数据检索模式。 在设计数据模型时,始终需要考虑数据的应用程序使用情况(即数据的查询,更新和处理)以及数据本身的固有结构。
灵活的 Schema
在关系型数据库中,必须在插入数据之前确定并声明表的结构。而 MongoDB 的 collection 默认情况下不需要其文档具有相同的架构。也就是说:
同一个 collection 中的 document 不需要具有相同的 field 集,并且 field 的数据类型可以在集合中的不同文档之间有所不同。
要更改 collection 中的 document 结构,例如添加新 field,删除现有 field 或将 field 值更改为新类型,只需要将文档更新为新结构即可。
这种灵活性有助于将 document 映射到实体或对象。每个 document 都可以匹配所表示实体的数据字段,即使该文档与集合中的其他文档有很大的不同。但是,实际上,集合中的文档具有相似的结构,并且您可以在更新和插入操作期间对 collection 强制执行 document 校验规则。
Document 结构
嵌入式数据模型
嵌入式 document 通过将相关数据存储在单个 document 结构中来捕获数据之间的关系。 MongoDB document 可以将 document 结构嵌入到另一个 document 中的字段或数组中。这些非规范化的数据模型允许应用程序在单个数据库操作中检索和操纵相关数据。

对于 MongoDB 中的很多场景,非规范化数据模型都是最佳的。
嵌入式 document 有大小限制:必须小于 16 MB。
如果是较大的二进制数据,可以考虑 GridFS。
引用式数据模型
引用通过包含从一个 document 到另一个 document 的链接或引用来存储数据之间的关系。 应用程序可以解析这些引用以访问相关数据。 广义上讲,这些是规范化的数据模型。
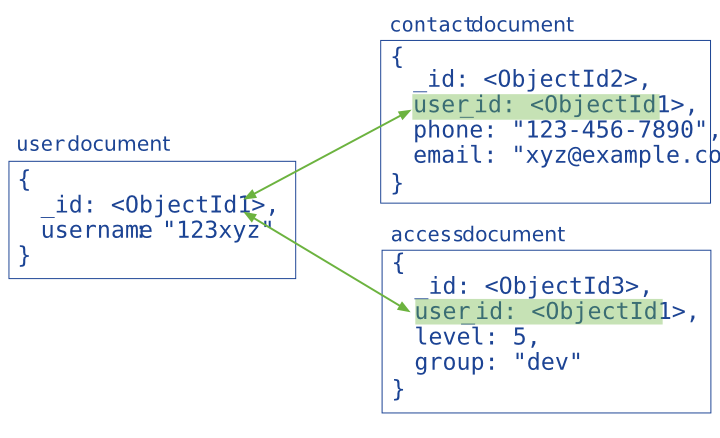
通常,在以下场景使用引用式的数据模型:
- 嵌入时会导致数据重复,但无法提供足够的读取性能优势,无法胜过重复的含义。
- 代表更复杂的多对多关系。
- 为大规模分层数据集建模。
为了 join collection,MongoDB 支持聚合 stage:
$lookup(MongoDB 3.2 开始支持)$graphLookup(MongoDB 3.4 开始支持)
MongoDB 还提供了引用来支持跨集合 join 数据:
- 引用数据模型示例,参考:Model One-to-Many Relationships with Document References.
- 更多树形模型,参考:Model Tree Structures.
原子写操作
单 document 的原子性
在 MongoDB 中,针对单个 document 的写操作是原子性的,即使该 document 中嵌入了多个子 document。 具有嵌入数据的非规范化数据模型将所有相关数据合并在一个 document 中,而不是在多个 document 和 collection 中进行规范化。 该数据模型有助于原子操作。 当单个写入操作(例如 db.collection.updateMany())修改多个 document 时,每个 document 的独立修改是原子的,但整个操作不是原子的。
多 document 事务
对于需要对多个 document(在单个或多个集合中)进行读写原子性的情况,MongoDB 支持多 document 事务。
- 在版本 4.0 中,MongoDB 在副本集上支持多 document 事务。
- 在版本 4.2 中,MongoDB 引入了分布式事务,它增加了对分片群集上多 document 事务的支持,并合并了对副本集上多 document 事务的现有支持。
在大多数情况下,多 document 事务会比单 document 的写入产生更高的性能消耗,并且多 document 事务的可用性不能替代高效的结构设计。 在许多情况下,非规范化数据模型(嵌入式 document 和数组)仍是最佳选择。 也就是说,合理的数据建模,将最大程度地减少对多 document 事务的需求。
数据使用和性能
在设计数据模型时,请考虑应用程序将如何使用您的数据库。 例如,如果您的应用程序仅使用最近插入的 document,请考虑使用上限集合。 或者,如果您的应用程序主要是对 collection 的读取操作,则添加索引以提高性能。
Schema 校验
指定校验规则
如果创建新 collection 时要指定校验规则,需要在使用 db.createCollection() 时指定 validator 选项。
如果要将 document 校验添加到现有 collection 中,需要使用带有 validator 选项的 collMod 命令。
MongoDB 还提供以下相关选项:
validationLevel选项(用于确定 MongoDB 在更新过程中,对现有 document 应用校验规则的严格程度)validationAction选项(用于确定 MongoDB 发现违反校验规则的 document 时,是选择报错并拒绝,还是接受数据但在日志中告警)。
JSON Schema
从 3.6 版本开始,MongoDB 开始支持 JSON Schema 校验。
可以通过在 validator 表达式中使用 $jsonSchema 操作来指定 JSON Schema 校验。
【示例】
db.createCollection('students', {
validator: {
$jsonSchema: {
bsonType: 'object',
required: ['name', 'year', 'major', 'address'],
properties: {
name: {
bsonType: 'string',
description: 'must be a string and is required',
},
year: {
bsonType: 'int',
minimum: 2017,
maximum: 3017,
description: 'must be an integer in [ 2017, 3017 ] and is required',
},
major: {
enum: ['Math', 'English', 'Computer Science', 'History', null],
description: 'can only be one of the enum values and is required',
},
gpa: {
bsonType: ['double'],
description: 'must be a double if the field exists',
},
address: {
bsonType: 'object',
required: ['city'],
properties: {
street: {
bsonType: 'string',
description: 'must be a string if the field exists',
},
city: {
bsonType: 'string',
description: 'must be a string and is required',
},
},
},
},
},
},
})其它查询表达式
除了使用 $jsonSchema 查询运算符的 JSON Schema 校验外,MongoDB 还支持其它查询运算符的校验,但以下情况除外:
【示例】查询表达式中指定校验规则
db.createCollection('contacts', {
validator: {
$or: [
{ phone: { $type: 'string' } },
{ email: { $regex: /@mongodb\.com$/ } },
{ status: { $in: ['Unknown', 'Incomplete'] } },
],
},
})行为
校验发生在更新和插入期间。添加校验规则到 collection 时,不会对现有的 document 进行校验,除非发生修改操作。
现有的 document
validationLevel 选项确定 MongoDB 进行规则校验时执行的操作:
- 如果
validationLevel是 strict(严格级别。这是 MongoDB 默认级别),则 MongoDB 将校验规则应用于所有插入和更新。 - 如果
validationLevel是 moderate(中等级别),则 MongoDB 只对已满足校验条件的现有文档的插入和更新操作进行校验;对不符合校验标准的现有文档的更新操作不进行校验。
【示例】
下面是一个正常的插入操作:
db.contacts.insert([
{
_id: 1,
name: 'Anne',
phone: '+1 555 123 456',
city: 'London',
status: 'Complete',
},
{ _id: 2, name: 'Ivan', city: 'Vancouver' },
])在 collection 上配置一个校验规则:
db.runCommand({
collMod: 'contacts',
validator: {
$jsonSchema: {
bsonType: 'object',
required: ['phone', 'name'],
properties: {
phone: {
bsonType: 'string',
description: 'must be a string and is required',
},
name: {
bsonType: 'string',
description: 'must be a string and is required',
},
},
},
},
validationLevel: 'moderate',
})则 contacts collection 现在添加了含中等级别(moderate) validationLevel 的 validator:
- 如果尝试更新
_id为 1 的文档,则 MongoDB 将应用校验规则,因为现有文档符合条件。 - 相反,MongoDB 不会将校验
_id为 2 的文档,因为它不符合校验规则。
如果要完全禁用校验,可以将 validationLevel 置为 off。
接受或拒绝无效的 document
- 如果 validationAction 是 Error(默认),则 MongoDB 拒绝任何违反校验规则的插入或更新。
- 如果 validationAction 是 Warn,MongoDB 会记录所有的违规,但允许进行插入或更新。
【示例】
创建集合时,配置 validationAction 为 warn。
db.createCollection('contacts2', {
validator: {
$jsonSchema: {
bsonType: 'object',
required: ['phone'],
properties: {
phone: {
bsonType: 'string',
description: 'must be a string and is required',
},
email: {
bsonType: 'string',
pattern: '@mongodb.com$',
description:
'must be a string and match the regular expression pattern',
},
status: {
enum: ['Unknown', 'Incomplete'],
description: 'can only be one of the enum values',
},
},
},
},
validationAction: 'warn',
})尝试插入一条违规记录
> db.contacts2.insert( { name: "Amanda", status: "Updated" } )
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })MongoDB 允许这条操作执行,但是服务器会记录下告警信息。
{"t":{"$date":"2020-09-11T16:35:57.754+08:00"},"s":"W", "c":"STORAGE", "id":20294, "ctx":"conn14","msg":"Document would fail validation","attr":{"namespace":"test.contacts2","document":{"_id":{"$oid":"5f5b36ed8ea53d62a0b51c4e"},"name":"Amanda","status":"Updated"}}}限制
不能在 admin、local、config 这几个特殊的数据库中指定校验规则。
不能在 system.* collection 中指定校验。










