tomcat启动流程
tomcat启动流程

tomcat源码目录
catalina目录
catalina包含所有的Servlet容器实现,以及涉及到安全、会话、集群、部署管理Servlet容器的各个方面,同时,它还包含了启动入口。
coyote目录
coyote是tomcat链接器框架的名称,是tomcat服务器提供的客户端访问的外部接口,客户端通过Coyote与服务器建立链接、发送请求并接收响应。
El目录,提供java表达式语言
Jasper模块提供JSP引擎
Naming模块提供JNDI的服务
Juli提供服务器日志的服务
tomcat提供外部调用的接口api
tomcat启动流程分析
启动流程解析:注意是标准的启动,也就是从bin目录下的启动文件中启动tomcat
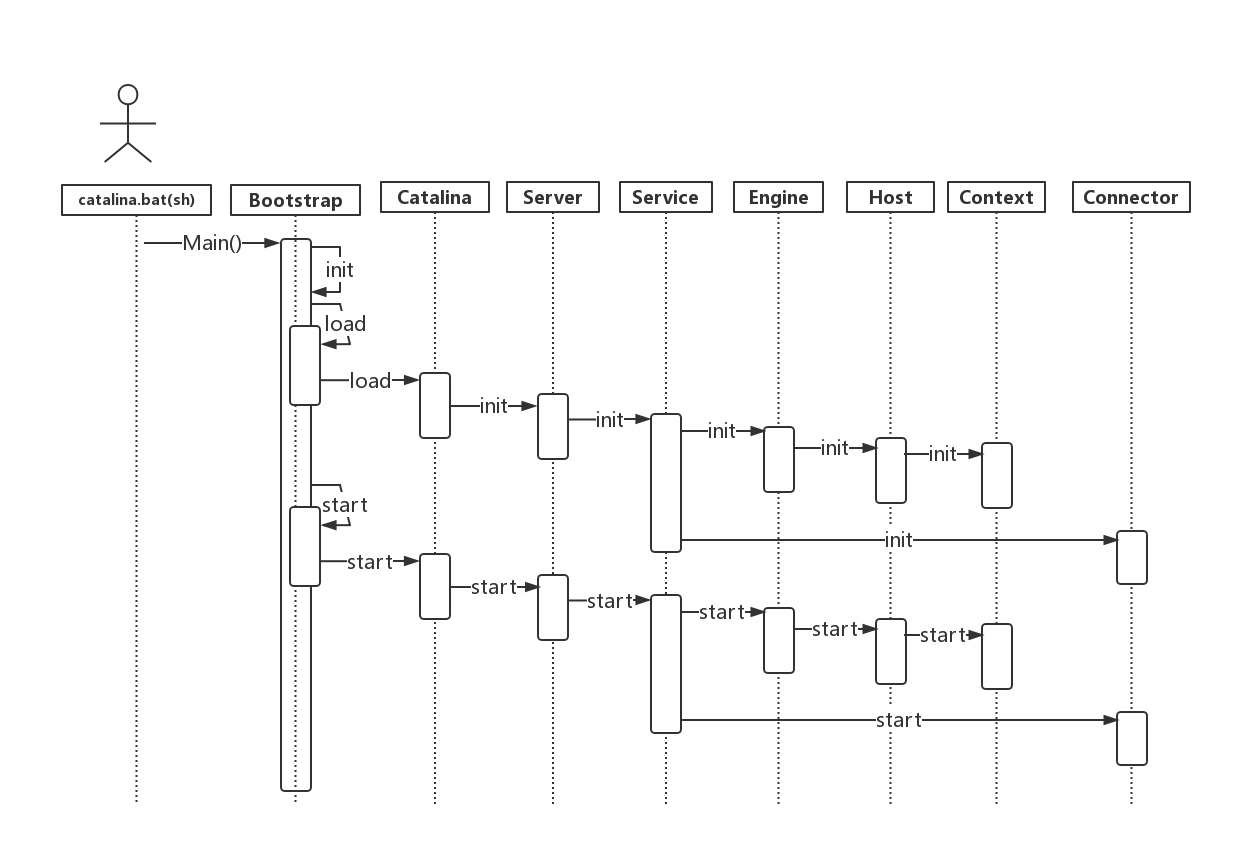 我们可以看到这个流程非常的清晰,同时注意到,tomcat的启动非常的标准,除去Boostrap和Catalin,我们可以对照一下Server.xml的配置文件。Server,service等等这些组件都是一一对照,同时又有先后顺序。
我们可以看到这个流程非常的清晰,同时注意到,tomcat的启动非常的标准,除去Boostrap和Catalin,我们可以对照一下Server.xml的配置文件。Server,service等等这些组件都是一一对照,同时又有先后顺序。基本的顺序是先init方法,然后再start方法。
加入调试信息():注意是标准的启动,也就是从bin目录下的启动文件中启动tomcat
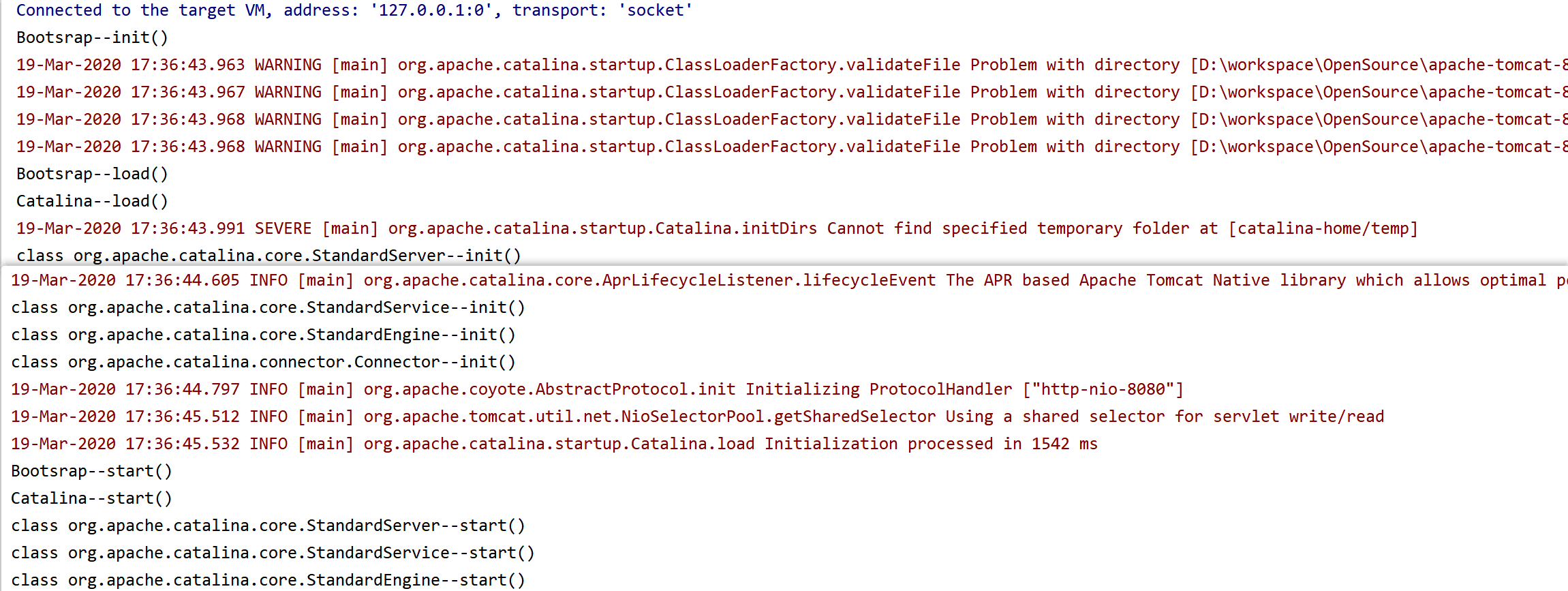
可以看到,在源码中加入调试的信息和流程图是一致的。
我们可以看到,除了Bootstrap和catalina类,其他的Server,service等等之类的都只是一个接口,实现类均为StandardXXX类。
我们来看下StandardServer类,
源码分析
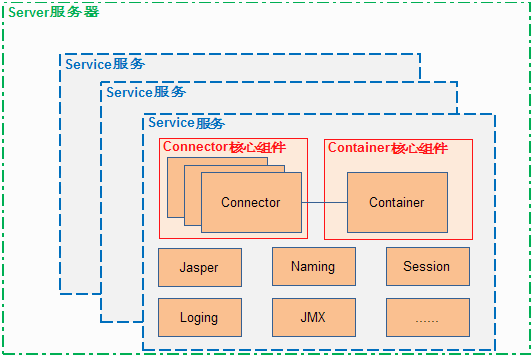
tomcat主要有两个核心的组件,一个是Connector(连接器)和容器。所谓连接器就是当有HTTP请求到来时,连接器负责接收这个请求,然后将该请求转发到容器。容器有Engine,Host,Context,Wrapper。Engine:表示整个Catalina servlet引擎;Host:表示包含一个或多个Context容器的虚拟主机;Context:表示一个Web应用程序。一个Context可以有多个Wrapper;Wrapper:表示一个独立的servlet。一个容器可以有0个或多个低层级的子容器。例如,一般情况下,一个Context实例会有一个或多个Wrapper实例。一个Host实例中会有0个或多个Context实例。但是,Wrapper类型处于层级结构的最底层,因此,它无法再包含子容器了。
Bootstrap启动类
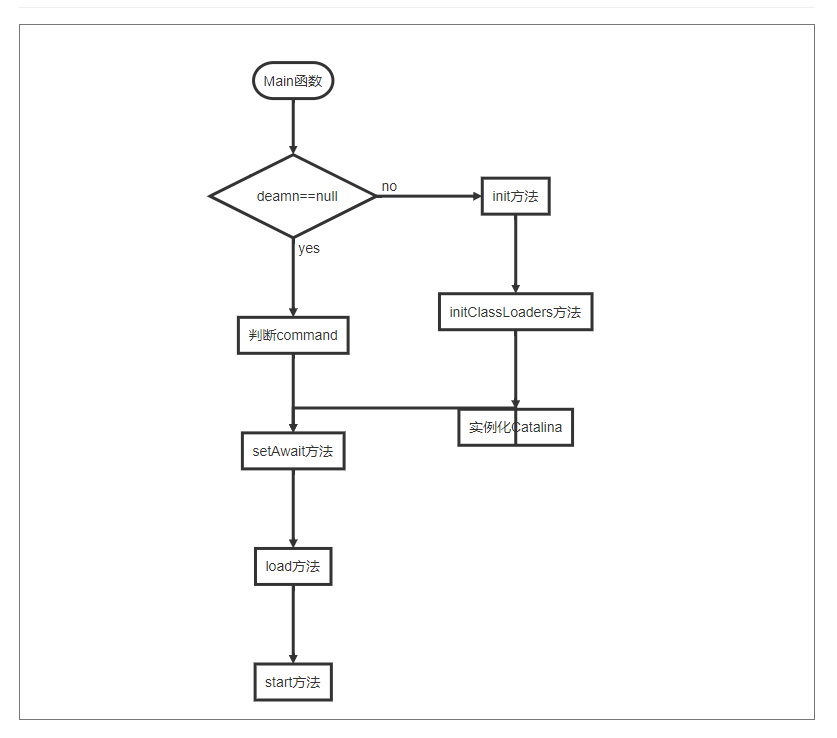
main
一般启动tomcat会是运行startup.bat或者startup.sh文件,这两个文件最后都会调用,org.apache.catalina.startup包下面Bootstrap类的main方法。main方法具体实现如下:
public static void main(String args[]) {
synchronized (daemonLock) {
if (daemon == null) {
// Don't set daemon until init() has completed
// 在init()完成之前不要设置守护进程
// 创建一个Bootstrap对象
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
try {
//调用初始化方法
// 初始化ClassLoader:
// ClassLoader commonLoader = null;
// ClassLoader catalinaLoader = null; 绑定到当前线程上
// ClassLoader sharedLoader = null;
// catalinaLoader类加载器创建Catalina实例,赋值给catalinaDaemon
bootstrap.init();
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
return;
}
daemon = bootstrap;
} else {
// When running as a service the call to stop will be on a new
// thread so make sure the correct class loader is used to
// prevent a range of class not found exceptions.
//设置线程的上下文类加载器为 catalinaLoader
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(daemon.catalinaLoader);
}
}
try {
// 默认执行 start 方法
String command = "start";
if (args.length > 0) {
command = args[args.length - 1];
}
if (command.equals("startd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "start";
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
} else if (command.equals("stopd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "stop";
daemon.stop();
} else if (command.equals("start")) {
// 执行这个位置,【让主线程不退出】
daemon.setAwait(true);
// 反射调用 catalinaDaemon#load 方法,根据server.xml 创建服务
daemon.load(args);
// 反射调用 catalinaDaemon#start 方法,启动服务
daemon.start();
if (null == daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
} else if (command.equals("stop")) {
daemon.stopServer(args);
} else if (command.equals("configtest")) {
daemon.load(args);
if (null == daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
System.exit(0);
} else {
log.warn("Bootstrap: command \"" + command + "\" does not exist.");
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Unwrap the Exception for clearer error reporting
if (t instanceof InvocationTargetException &&
t.getCause() != null) {
t = t.getCause();
}
//处理异常
handleThrowable(t);
t.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
}main方法中,首先执行init方法初始化了tomcat自己的类加载器,并通过类加载器创建Catalina实例,然后赋给catalinaDaemon变量,后续操作都使用catalinaDaemon来执行。
setAwait
后面默认执行start命令,将调用setAwait(true),load(args)和start()这三个方法,这三个方法内部都通过反射调用了Catalina的相应方法。
// org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina
public void setAwait(boolean b) {
await = b;
}setAwait方法用于设置Server启动完成后是否进入等待状态的标志,如果为true则进入,否则不进入。
init
main方法先实例化了一个Bootstrap实例,接着调用了init方法。init方法是生命周期方法,以后不再累述。接着看init的具体实现。
public void init() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Bootsrap--init()");
//类加载器初始化
initClassLoaders();
//设置线程的上下文类加载器来解决有可能的ClassNotFoundException问题
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader);
SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader);
// Load our startup class and call its process() method
// 加载启动类Catalina并调用其process()方法
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Loading startup class");
//加载Catalina类
Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
// Set the shared extensions class loader
// 设置共享扩展类加载器sharedLoader
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Setting startup class properties");
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
//通过反射调用setParentClassLoader方法将java.lang.ClassLoader设置为Catalina的父类加载器
Method method =
startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
//完成方法调用
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance;
}initClassLoaders
init方法,先初始化了类加载器。initClassLoaders方法具体实现如下:
//初始化三个类加载器以及确定父子关系
private void initClassLoaders() {
try {
// commonLoader的加载路径为common.loader
commonLoader = createClassLoader("common", null);
if (commonLoader == null) {
// no config file, default to this loader - we might be in a 'single' env.
commonLoader = this.getClass().getClassLoader();
}
// 加载路径为server.loader,默认为空,父类加载器为commonLoader
catalinaLoader = createClassLoader("server", commonLoader);
// 加载路径为shared.loader,默认为空,父类加载器为commonLoader
sharedLoader = createClassLoader("shared", commonLoader);
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleThrowable(t);
log.error("Class loader creation threw exception", t);
System.exit(1);
}
}createClassLoader
createClassLoader是通过工厂模式创建类加载器,从conf目录中的catalina.properties属性文件中读取配置来设置某一个类加载器加载那些jar包的文件
//创建类加载器
private ClassLoader createClassLoader(String name, ClassLoader parent)
throws Exception {
// catalinaLoader与sharedLoader的加载路径均为空,所以直接返回commonLoader对象,默认3者为同一个对象
String value = CatalinaProperties.getProperty(name + ".loader");
if ((value == null) || (value.equals("")))
return parent;
value = replace(value);
List<Repository> repositories = new ArrayList<>();
String[] repositoryPaths = getPaths(value);
for (String repository : repositoryPaths) {
// Check for a JAR URL repository
// 检查一个jar的URL仓库
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
URL url = new URL(repository);
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.URL));
continue;
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
// Ignore
//为了防止因为一个jar的加载失败导致整个系统启动失败所以吞掉异常
}
// Local repository
// 本地仓库 jar
if (repository.endsWith("*.jar")) {
repository = repository.substring
(0, repository.length() - "*.jar".length());
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.GLOB));
} else if (repository.endsWith(".jar")) {
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.JAR));
} else {
repositories.add(new Repository(repository, RepositoryType.DIR));
}
}
//通过工厂模式创建类加载器
return ClassLoaderFactory.createClassLoader(repositories, parent);
}createClassLoader需要传入一个父加载器。从具体的代码中可以看出,commonLoader类加载器是catalinaLoader类加载器和sharedLoader类加载器的父加载器。初始化完类加载器后,使用反射机制调用org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina类下的setParentClassLoader方法。具体代码是:
// Load our startup class and call its process() method
// 加载启动类Catalina并调用其process()方法
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Loading startup class");
//加载Catalina类
Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina");
Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance();
// Set the shared extensions class loader
// 设置共享扩展类加载器sharedLoader
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Setting startup class properties");
String methodName = "setParentClassLoader";
Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader");
Object paramValues[] = new Object[1];
paramValues[0] = sharedLoader;
//通过反射调用setParentClassLoader方法将java.lang.ClassLoader设置为Catalina的父类加载器
Method method =
startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
//完成方法调用
method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues);因为tomcat执行的是start操作,调用完init方法后,会执行load方法。
if (command.equals("startd")) {
args[args.length - 1] = "start";
daemon.load(args);
daemon.start();
}load
load方法通过反射调用Catalina类的load方法。
private void load(String[] arguments) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Bootsrap--load()");
// Call the load() method
String methodName = "load";
Object param[];
Class<?> paramTypes[];
if (arguments == null || arguments.length == 0) {
paramTypes = null;
param = null;
} else {
paramTypes = new Class[1];
paramTypes[0] = arguments.getClass();
param = new Object[1];
param[0] = arguments;
}
//获取catalina类的load方法
Method method =
catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Calling startup class " + method);
}
//通过反射完成调用
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, param);
}Catalina
Catalina 的主要任务就是创建 Server,它不是直接 new 一个 Server 实例就完事了,而是需要解析 server.xml,把在 server.xml 里配置的各种组件一一创建出来,接着调用 Server 组件的 init 方法和 start 方法,这样整个 tomcat 就启动起来了。作为“管理者”,Catalina 还需要处理各种“异常”情况,比如当我们通过“Ctrl + C”关闭 tomcat 时,tomcat 将如何优雅的停止并且清理资源呢?因此 Catalina 在 JVM 中注册一个“关闭钩子”。
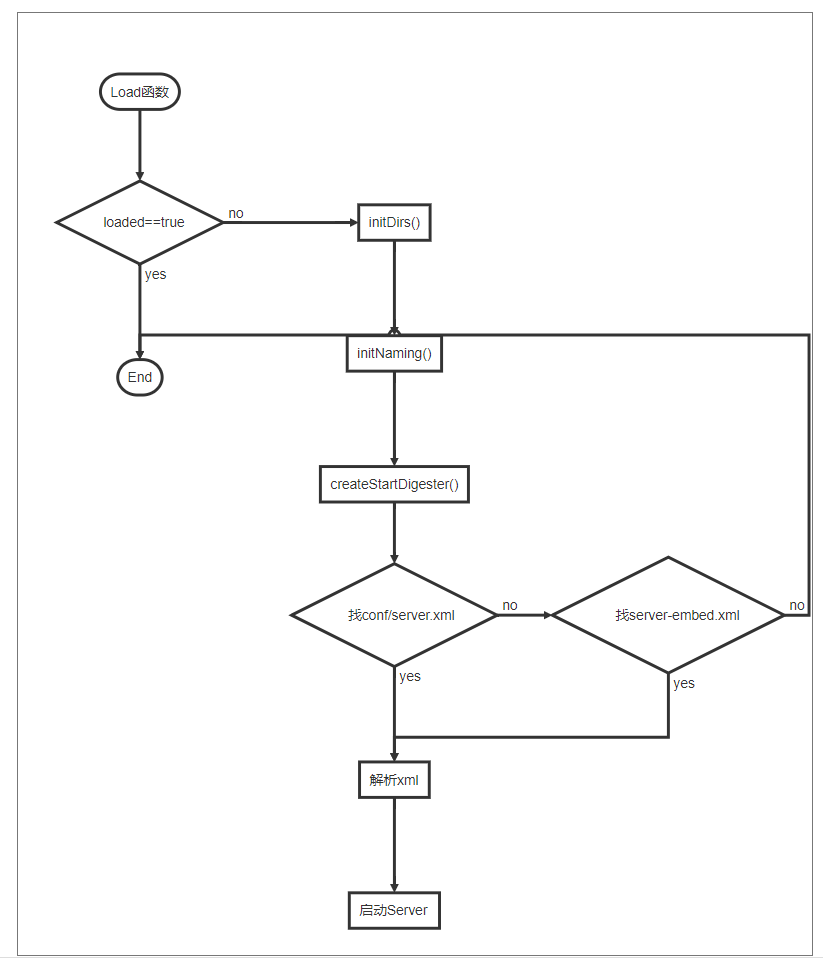
load
Catalina的load方法根据conf/server.xml创建了Server对象,并赋值给server属性(具体是通过开源项目Digester完成的),然后调用了server的init方法。
public void load() {
System.out.println("Catalina--load()");
// 已经加载就返回
if (loaded) {
return;
}
// 设置加载状态
loaded = true;
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
//初始化一些临时文件夹
initDirs();
// Before digester - it may be needed
//初始化JNDI服务
initNaming();
// Create and execute our Digester
// 通过 digester 解析 server.xml 配置文件
//创建并执行Digester来读取conf/server.xml文件
Digester digester = createStartDigester();
InputSource inputSource = null;
InputStream inputStream = null;
File file = null;
try {
try {
// 默认指定了 conf/server.xml
file = configFile();
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
inputSource = new InputSource(file.toURI().toURL().toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail", file), e);
}
}
//读取conf/server.xml的数据
if (inputStream == null) {
try {
inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream(getConfigFile());
inputSource = new InputSource
(getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResource(getConfigFile()).toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
getConfigFile()), e);
}
}
}
// This should be included in catalina.jar
// Alternative: don't bother with xml, just create it manually.
if (inputStream == null) {
try {
// 尝试加载 server-embed.xml
inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("server-embed.xml");
inputSource = new InputSource
(getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResource("server-embed.xml").toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
"server-embed.xml"), e);
}
}
}
// 依旧找不到文件,返回
if (inputStream == null || inputSource == null) {
if (file == null) {
log.warn(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
getConfigFile() + "] or [server-embed.xml]"));
} else {
log.warn(sm.getString("catalina.configFail",
file.getAbsolutePath()));
if (file.exists() && !file.canRead()) {
log.warn("Permissions incorrect, read permission is not allowed on the file.");
}
}
return;
}
try {
inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream);
digester.push(this);
// 解析 xml
digester.parse(inputSource);
} catch (SAXParseException spe) {
log.warn("Catalina.start using " + getConfigFile() + ": " +
spe.getMessage());
return;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Catalina.start using " + getConfigFile() + ": " , e);
return;
}
} finally {
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
// 在 static中定义,
//获取server类完成一些设置
getServer().setCatalina(this);
getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile());
getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile());
// Stream redirection
initStreams();
// Start the new server
try {
// 创建 Server
//经过Digester这里的Server已经是StandardServer ,但是StandardServer类中没有init方法
getServer().init();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE")) {
throw new java.lang.Error(e);
} else {
log.error("Catalina.start", e);
}
}
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
if(log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("Initialization processed in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");
}
}createStartDigester
load方法中比较重要的方法是createStartDigester(),createStartDigester方法主要的作用就是帮我们实例化了所有的服务组件包括server,service和connect。具体的实例化方法
Digester 查相关资料:Java解析xml主要由DOM4J(一次读取到内存并解析)、SAX(一次解析一部分),digester本身采用SAX的解析方式,并提供了一层包装,对使用者更加友好,后来独立出来成为apache的Commons下面的一个单独的子项目。
protected Digester createStartDigester() {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
// Initialize the digester
Digester digester = new Digester();
digester.setValidating(false);
digester.setRulesValidation(true);
Map<Class<?>, List<String>> fakeAttributes = new HashMap<>();
List<String> objectAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
objectAttrs.add("className");
fakeAttributes.put(Object.class, objectAttrs);
// Ignore attribute added by Eclipse for its internal tracking
List<String> contextAttrs = new ArrayList<>();
contextAttrs.add("source");
fakeAttributes.put(StandardContext.class, contextAttrs);
digester.setFakeAttributes(fakeAttributes);
digester.setUseContextClassLoader(true);
// Configure the actions we will be using
digester.addObjectCreate("Server",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server");
digester.addSetNext("Server",
"setServer",
"org.apache.catalina.Server");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/GlobalNamingResources",
"org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResourcesImpl");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/GlobalNamingResources");
digester.addSetNext("Server/GlobalNamingResources",
"setGlobalNamingResources",
"org.apache.catalina.deploy.NamingResourcesImpl");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service",
"addService",
"org.apache.catalina.Service");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
//Executor
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Executor",
"org.apache.catalina.core.StandardThreadExecutor",
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Executor");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Executor",
"addExecutor",
"org.apache.catalina.Executor");
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector",
new ConnectorCreateRule());
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector",
new SetAllPropertiesRule(new String[]{"executor", "sslImplementationName"}));
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector",
"addConnector",
"org.apache.catalina.connector.Connector");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.SSLHostConfig");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig",
"addSslHostConfig",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.SSLHostConfig");
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/Certificate",
new CertificateCreateRule());
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/Certificate",
new SetAllPropertiesRule(new String[]{"type"}));
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/Certificate",
"addCertificate",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.SSLHostConfigCertificate");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.openssl.OpenSSLConf");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf",
"setOpenSslConf",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.openssl.OpenSSLConf");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf/OpenSSLConfCmd",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.openssl.OpenSSLConfCmd");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf/OpenSSLConfCmd");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/SSLHostConfig/OpenSSLConf/OpenSSLConfCmd",
"addCmd",
"org.apache.tomcat.util.net.openssl.OpenSSLConfCmd");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/Listener",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/Listener");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/Listener",
"addLifecycleListener",
"org.apache.catalina.LifecycleListener");
digester.addObjectCreate("Server/Service/Connector/UpgradeProtocol",
null, // MUST be specified in the element
"className");
digester.addSetProperties("Server/Service/Connector/UpgradeProtocol");
digester.addSetNext("Server/Service/Connector/UpgradeProtocol",
"addUpgradeProtocol",
"org.apache.coyote.UpgradeProtocol");
// Add RuleSets for nested elements
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/GlobalNamingResources/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new EngineRuleSet("Server/Service/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new HostRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/"));
digester.addRuleSet(new ContextRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/"));
addClusterRuleSet(digester, "Server/Service/Engine/Host/Cluster/");
digester.addRuleSet(new NamingRuleSet("Server/Service/Engine/Host/Context/"));
// When the 'engine' is found, set the parentClassLoader.
digester.addRule("Server/Service/Engine",
new SetParentClassLoaderRule(parentClassLoader));
addClusterRuleSet(digester, "Server/Service/Engine/Cluster/");
long t2=System.currentTimeMillis();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Digester for server.xml created " + ( t2-t1 ));
}
return digester;
}start
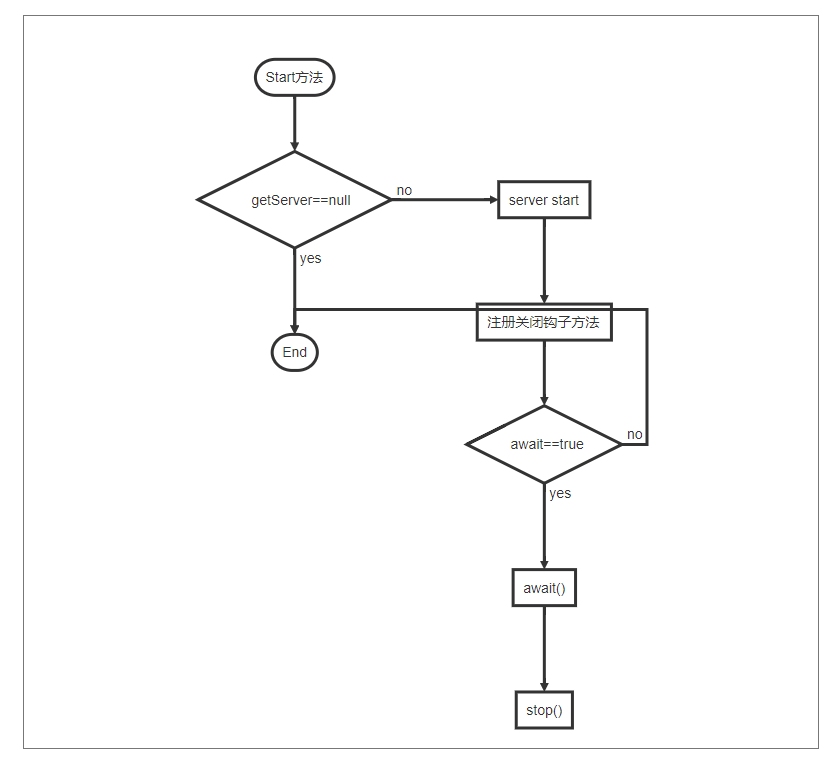
初始化操作完成后,接下来会执行catalina实例的start方法。
public void start() {
System.out.println("Catalina--start()");
// 1. 如果持有的 Server 实例为空,就解析 server.xml 创建出来
if (getServer() == null) {
load();
}
// 2. 如果创建失败,报错退出
if (getServer() == null) {
log.fatal("Cannot start server. Server instance is not configured.");
return;
}
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// Start the new server
try {
// 调用Server的start方法启动服务器
getServer().start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.serverStartFail"), e);
try {
getServer().destroy();
} catch (LifecycleException e1) {
log.debug("destroy() failed for failed Server ", e1);
}
return;
}
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
if(log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("Server startup in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");
}
// Register shutdown hook
// 注册 关闭 钩子方法
if (useShutdownHook) {
if (shutdownHook == null) {
shutdownHook = new CatalinaShutdownHook();
}
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
// If JULI is being used, disable JULI's shutdown hook since
// shutdown hooks run in parallel and log messages may be lost
// if JULI's hook completes before the CatalinaShutdownHook()
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(
false);
}
}
// 此处判断 主线程是否await
if (await) {
// 在 StandardServer 中调用,用来监听 8005 端口,
// 收到 SHUTDOWN 命令关闭 Server
await();
stop();
}
}那什么是“关闭钩子”,它又是做什么的呢?如果我们需要在 JVM 关闭时做一些清理工作,比如将缓存数据刷到磁盘上,或者清理一些临时文件,可以向 JVM 注册一个“关闭钩子”。“关闭钩子”其实就是一个线程,JVM 在停止之前会尝试执行这个线程的 run 方法。下面我们来看看 tomcat 的“关闭钩子”CatalinaShutdownHook 做了些什么。
protected class CatalinaShutdownHook extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if (getServer() != null) {
Catalina.this.stop();
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
...
}
}
}从这段代码中你可以看到,tomcat 的“关闭钩子”实际上就执行了 Server 的 stop 方法,Server 的 stop 方法会释放和清理所有的资源。
StandardServer
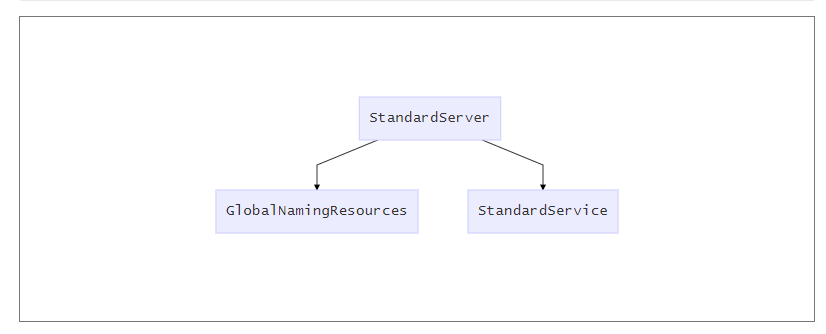

从上面加载的组件中,tomcat会默认加载org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer作为Server的实例类。
addService
Server 组件的具体实现类是 StandardServer。Server 继承了 LifeCycleBase,它的生命周期被统一管理,并且它的子组件是 Service,因此它还需要管理 Service 的生命周期,也就是说在启动时调用 Service 组件的启动方法,在停止时调用它们的停止方法。Server 在内部维护了若干 Service 组件,它是以数组来保存的,那 Server 是如何添加一个 Service 到数组中的呢?
@Override
public void addService(Service service) {
service.setServer(this);
synchronized (servicesLock) {
// 创建一个长度 +1 的新数组
Service results[] = new Service[services.length + 1];
// 将老的数据复制过去
System.arraycopy(services, 0, results, 0, services.length);
results[services.length] = service;
services = results;
// 启动 Service 组件
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
try {
service.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
// 触发监听事件
support.firePropertyChange("service", null, service);
}
}从上面的代码你能看到,它并没有一开始就分配一个很长的数组,而是在添加的过程中动态地扩展数组长度,当添加一个新的 Service 实例时,会创建一个新数组并把原来数组内容复制到新数组,这样做的目的其实是为了节省内存空间。
initInternal
因为StandardServer使用了Lifecycle生命周期管理,调用init会调用到LifecycleBase的init方法,并会调用到StandardServer的initInternal方法。
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Register global String cache
// Note although the cache is global, if there are multiple Servers
// present in the JVM (may happen when embedding) then the same cache
// will be registered under multiple names
// 注册全局 String cache
onameStringCache = register(new StringCache(), "type=StringCache");
// Register the MBeanFactory
// 注册 MBeanFactory
MBeanFactory factory = new MBeanFactory();
factory.setContainer(this);
onameMBeanFactory = register(factory, "type=MBeanFactory");
// Register the naming resources
// 注册命名资源
globalNamingResources.init();
// Populate the extension validator with JARs from common and shared
// class loaders
if (getCatalina() != null) {
ClassLoader cl = getCatalina().getParentClassLoader();
// Walk the class loader hierarchy. Stop at the system class loader.
// This will add the shared (if present) and common class loaders
while (cl != null && cl != ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()) {
if (cl instanceof URLClassLoader) {
URL[] urls = ((URLClassLoader) cl).getURLs();
for (URL url : urls) {
if (url.getProtocol().equals("file")) {
try {
File f = new File (url.toURI());
if (f.isFile() &&
f.getName().endsWith(".jar")) {
ExtensionValidator.addSystemResource(f);
}
} catch (URISyntaxException e) {
// Ignore
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
}
cl = cl.getParent();
}
}
// Initialize our defined Services
// 初始化定义的所有 Service
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].init();
}
}startInternal
因为StandardServer使用了Lifecycle生命周期管理,调用start会调用到LifecycleBase的start方法,并会调用到StandardServer的startInternal方法。
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// 设置状态
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
// 触发事件
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
globalNamingResources.start();
// Start our defined Services
//启动所有的service
synchronized (servicesLock) {
for (int i = 0; i < services.length; i++) {
services[i].start();
}
}
}await
在 await 方法里会创建一个 Socket 监听 8005 端口,并在一个死循环里接收 Socket 上的连接请求,如果有新的连接到来就建立连接,然后从 Socket 中读取数据;如果读到的数据是停止命令“SHUTDOWN”,就退出循环,进入 stop 流程。
@Override
public void await() {
try {
// port 默认 8005
awaitSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1,
InetAddress.getByName(address));
} catch (IOException e) {
return;
}
// 匹配 SHUTDOWN 命令,用来关闭服务器
boolean match = command.toString().equals(shutdown);
if (match) {
break;
}
ServerSocket serverSocket = awaitSocket;
awaitThread = null;
awaitSocket = null;
// 关闭Server socket并返回
if (serverSocket != null) {
serverSocket.close();
}
}StandardService
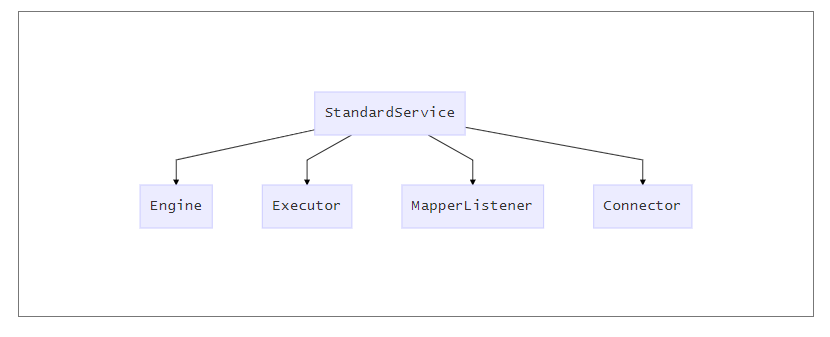
Service 组件的具体实现类是 StandardService,我们先来看看它的定义以及关键的成员变量。
public class StandardService extends LifecycleBase implements Service {
// 名字
private String name = null;
//Server 实例
private Server server = null;
// 连接器数组
protected Connector connectors[] = new Connector[0];
private final Object connectorsLock = new Object();
// 对应的 Engine 容器
private Engine engine = null;
// 映射器及其监听器
protected final Mapper mapper = new Mapper();
protected final MapperListener mapperListener = new MapperListener(this);
} StandardService 继承了 LifecycleBase 抽象类,此外 StandardService 中还有一些我们熟悉的组件,比如 Server、Connector、Engine 和 Mapper。
那为什么还有一个 MapperListener?这是因为 tomcat 支持热部署,当 Web 应用的部署发生变化时,Mapper 中的映射信息也要跟着变化,MapperListener 就是一个监听器,它监听容器的变化,并把信息更新到 Mapper 中,这是典型的观察者模式。
作为“管理”角色的组件,最重要的是维护其他组件的生命周期。此外在启动各种组件时,要注意它们的依赖关系,也就是说,要注意启动的顺序。
initInternal
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Engine初始化,一个Service对应一个Engine
if (engine != null) {
engine.init();
}
// Initialize any Executors
// 初始化Executor,默认 不会执行
for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) {
if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) {
((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain());
}
executor.init();
}
// Initialize mapper listener
// 初始化 MapperListener , 默认 LifecycleMBeanBase.java
mapperListener.init();
// Initialize our defined Connectors
// 初始化 Connector,server.xml 配置的 Connector
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector : connectors) {
try {
connector.init();
} catch (Exception e) {
String message = sm.getString(
"standardService.connector.initFailed", connector);
log.error(message, e);
if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE"))
throw new LifecycleException(message);
}
}
}
}startInternal
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if(log.isInfoEnabled())
log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name));
//1. 触发启动监听器
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our defined Container first
//2. 先启动 Engine,Engine 会启动它子容器
if (engine != null) {
synchronized (engine) {
engine.start();
}
}
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor: executors) {
executor.start();
}
}
//3. 再启动 Mapper 监听器
mapperListener.start();
// Start our defined Connectors second
//4. 最后启动连接器,连接器会启动它子组件,比如 Endpoint
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector: connectors) {
try {
// If it has already failed, don't try and start it
if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) {
//启动连接器
connector.start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"standardService.connector.startFailed",
connector), e);
}
}
}
}从启动方法可以看到,Service 先启动了 Engine 组件,再启动 Mapper 监听器,最后才是启动连接器。这很好理解,因为内层组件启动好了才能对外提供服务,才能启动外层的连接器组件。而 Mapper 也依赖容器组件,容器组件启动好了才能监听它们的变化,因此 Mapper 和 MapperListener 在容器组件之后启动。组件停止的顺序跟启动顺序正好相反的,也是基于它们的依赖关系。
ContainerBase
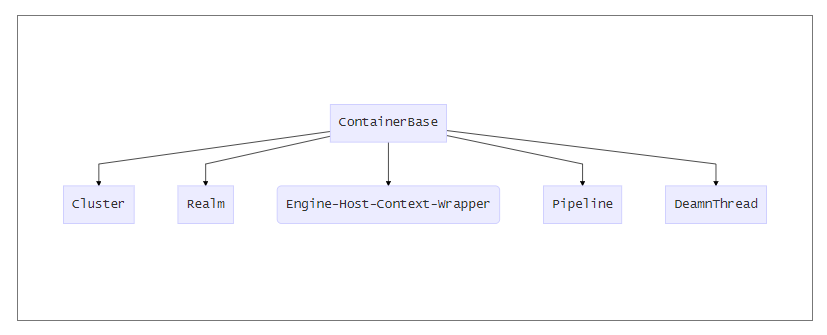
是容器的抽象父类,定义了容器生命周期中公共方法。Engine、Host、Context、Wrapper继承此父类。
继承关系

容器的作用
Container的4个容器是逐层包含的关系。它们之间的关系如下图:
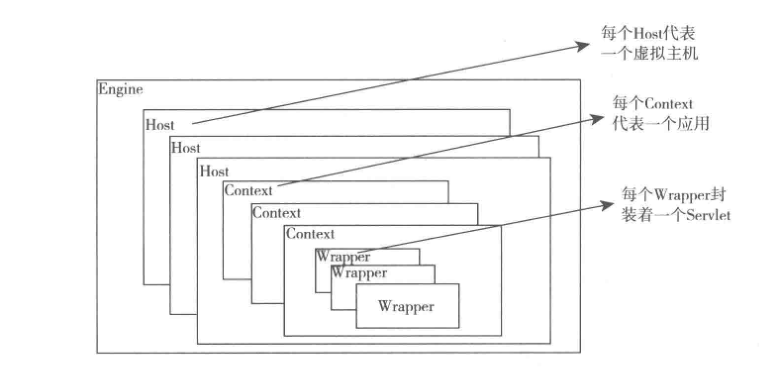
1、Engine:用来管理多个站点,一个Service最多只能有一个Engine。
2、Host:代表一个站点,通过配置Host可以添加站点。
3、Context:代表一个应用程序,对应一个WEB-INF目录。
4、Wrapper:每个Wrapper封装一个Servlet。
initInternal
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// 创建 线程池
BlockingQueue<Runnable> startStopQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
startStopExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
getStartStopThreadsInternal(),
getStartStopThreadsInternal(), 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
startStopQueue,
new StartStopThreadFactory(getName() + "-startStop-"));
startStopExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
super.initInternal();
}startInternal
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start our subordinate components, if any
logger = null;
getLogger();
// 如果有 Cluster和 Realm则调用其 start 方法
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
}
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
}
// Start our child containers, if any
// 通过 Future 调用所有子容器的 start方法
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(children[i])));
}
MultiThrowable multiThrowable = null;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
// 获取子容器 start 方法结果
result.get();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
if (multiThrowable == null) {
multiThrowable = new MultiThrowable();
}
multiThrowable.add(e);
}
}
if (multiThrowable != null) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"),
multiThrowable.getThrowable());
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
// 启用管道,后面介绍到
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
// 设置状态值
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our thread
// 启动后台线程,日志输出等工作,
threadStart();
}threadStart
开启后台线程,定时检查 session 超时、
protected void threadStart() {
if (thread != null)
return;
if (backgroundProcessorDelay <= 0)
return;
threadDone = false;
String threadName = "ContainerBackgroundProcessor[" + toString() + "]";
thread = new Thread(new ContainerBackgroundProcessor(), threadName);
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
}processChildren
内部类 ContainerBackgroundProcessor, 默认 10s一次
在 StandardEngine 构造函数中定义
protected void processChildren(Container container) {
ClassLoader originalClassLoader = null;
try {
if (container instanceof Context) {
Loader loader = ((Context) container).getLoader();
// Loader will be null for FailedContext instances
if (loader == null) {
return;
}
// Ensure background processing for Contexts and Wrappers
// is performed under the web app's class loader
originalClassLoader = ((Context) container).bind(false, null);
}
container.backgroundProcess();
Container[] children = container.findChildren();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (children[i].getBackgroundProcessorDelay() <= 0) {
processChildren(children[i]);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error("Exception invoking periodic operation: ", t);
} finally {
if (container instanceof Context) {
((Context) container).unbind(false, originalClassLoader);
}
}
}backgroundProcess
@Override
public void backgroundProcess() {
if (!getState().isAvailable())
return;
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster != null) {
try {
cluster.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.cluster",
cluster), e);
}
}
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm != null) {
try {
realm.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.realm", realm), e);
}
}
Valve current = pipeline.getFirst();
while (current != null) {
try {
current.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.valve", current), e);
}
current = current.getNext();
}
fireLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.PERIODIC_EVENT, null);
}容器的配置
Server配置
<Server port="8005" shutdown="SHUTDOWN">
<Service name="Catalina">
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
<!-- Define an AJP 1.3 Connector on port 8009 -->
<Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" />
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost">
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">
</Host>
</Engine>
</Service>
</Server>- Server 在 8005端口监听关闭命令“SHUTDOWN”;
- Server 中定义了一个 Catalina的Service;
- Service 中定义了两个Connector:
- 一个是HTTP协议;
- 一个是AJP协议(用于集成);
- Service 中还定义了了一个Catalina的Engine;
- Engine 中定义了 localhost 的 Host;
- defaultHost:请求的域名如果在所有的Host的name和Alias中都找不到使用的默认值
- Host:
- name:表示域名;
- appBase:站点的位置;
- unpackWARS:是否自动解压war包;
- autoDeploy:是否自动部署;
- 子标签: excelib.com:给localhost定义别名;
Context配置
Context通过文件配置的方式一共有5个位置可以配置:
- conf/server.xml中的Context标签;
- conf/[enginename]/[hostname]/目录下以应用命名的 xml 文件。
- 应用自己的 /META-INT/context.xml;
- conf/context.xml 文件
- conf/[enginename]/[hostname]/context.xml.default文件;
用于全局配置
前三个用于配置单独的应用,后面2种是Context共享的。第4种是 整个 tomcat 共享,第5种配置的内容在对应的站点(Host)中共享。第1种方式只有在tomcat重启才会重新加载,不推荐使用。
<!--
用于全局配置
The contents of this file will be loaded for each web application
-->
<Context>
<!-- Default set of monitored resources. If one of these changes, the -->
<!-- web application will be reloaded. -->
<WatchedResource>WEB-INF/web.xml</WatchedResource>
<WatchedResource>${catalina.base}/conf/web.xml</WatchedResource>
</Context>Wrapper的配置
Wrapper的配置,在web.xml中配置的Servlet,一个Servlet对应一个Wrapper、可以在 conf/web.xml 中配置全局的 Wrapper,处理 Jsp的 JspServlet的配置等。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>fork</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>xpoweredBy</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>3</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>jsp</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.jsp</url-pattern>
<url-pattern>*.jspx</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--配置了 session 超时时间-->
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
<!-- 很多 mime 类型 -->
<mime-mapping>
</mime-mapping>LifecycleBase
fireLifecycleEvent
protected void fireLifecycleEvent(String type, Object data) {
LifecycleEvent event = new LifecycleEvent(this, type, data);
for (LifecycleListener listener : lifecycleListeners) {
listener.lifecycleEvent(event);
}
}HostConfig
lifecycleEvent
@Override
public void lifecycleEvent(LifecycleEvent event) {
// Identify the host we are associated with
try {
host = (Host) event.getLifecycle();
if (host instanceof StandardHost) {
setCopyXML(((StandardHost) host).isCopyXML());
setDeployXML(((StandardHost) host).isDeployXML());
setUnpackWARs(((StandardHost) host).isUnpackWARs());
setContextClass(((StandardHost) host).getContextClass());
}
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("hostConfig.cce", event.getLifecycle()), e);
return;
}
// Process the event that has occurred
if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.PERIODIC_EVENT)) {
// 是否自动部署
check();
} else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT)) {
beforeStart();
} else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.START_EVENT)) {
start();
} else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.STOP_EVENT)) {
stop();
}
}StandardEngine
Engine 本质是一个容器,因此它继承了 ContainerBase 基类,并且实现了 Engine 接口。
public class StandardEngine extends ContainerBase implements Engine {
}我们知道,Engine 的子容器是 Host,所以它持有了一个 Host 容器的数组,这些功能都被抽象到了 ContainerBase 中,ContainerBase 中有这样一个数据结构:
protected final HashMap<String, Container> children = new HashMap<>();ContainerBase 用 HashMap 保存了它的子容器,并且 ContainerBase 还实现了子容器的“增删改查”,甚至连子组件的启动和停止都提供了默认实现,比如 ContainerBase 会用专门的线程池来启动子容器。
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(children[i])));
}所以 Engine 在启动 Host 子容器时就直接重用了这个方法。
那 Engine 自己做了什么呢?我们知道容器组件最重要的功能是处理请求,而 Engine 容器对请求的“处理”,其实就是把请求转发给某一个 Host 子容器来处理,具体是通过 Valve 来实现的。
构造方法
public StandardEngine() {
super();
// pipeline 设置 basicValve
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardEngineValve());
setJvmRoute(System.getProperty("jvmRoute"));
// 设置等待时间 10
backgroundProcessorDelay = 10;
}initInternal
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Ensure that a Realm is present before any attempt is made to start
// one. This will create the default NullRealm if necessary.
// 没有定义 Realm ,设置一个 NullRealm,权限访问。
getRealm();
super.initInternal();
}startInternal
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Log our server identification information
if(log.isInfoEnabled())
log.info( "Starting Servlet Engine: " + ServerInfo.getServerInfo());
// Standard container startup
super.startInternal();
}StandardHost
构造方法
public StandardHost() {
super();
// 设置 BasicValve
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardHostValve());
}startInternal
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Set error report valve
// 设置 error Valve
String errorValve = getErrorReportValveClass();
if ((errorValve != null) && (!errorValve.equals(""))) {
try {
boolean found = false;
Valve[] valves = getPipeline().getValves();
for (Valve valve : valves) {
if (errorValve.equals(valve.getClass().getName())) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if(!found) {
// 绑定 errorValve
Valve valve =
(Valve) Class.forName(errorValve).getConstructor().newInstance();
getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString(
"standardHost.invalidErrorReportValveClass",
errorValve), t);
}
}
super.startInternal();
}StandardContext
构造方法
public StandardContext() {
super();
// 设置 BasicValve
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardContextValve());
// 广播通知
broadcaster = new NotificationBroadcasterSupport();
// Set defaults
if (!Globals.STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE) {
// Strict servlet compliance requires all extension mapped servlets
// to be checked against welcome files
resourceOnlyServlets.add("jsp");
}
}startInternal
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if(log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Starting " + getBaseName());
// Send j2ee.state.starting notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.state.starting",
this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber.getAndIncrement());
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
setConfigured(false);
boolean ok = true;
// Currently this is effectively a NO-OP but needs to be called to
// ensure the NamingResources follows the correct lifecycle
// namingResources 启动
if (namingResources != null) {
namingResources.start();
}
// Post work directory
postWorkDirectory();
// Add missing components as necessary
if (getResources() == null) { // (1) Required by Loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Configuring default Resources");
try {
setResources(new StandardRoot(this));
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.resourcesInit"), e);
ok = false;
}
}
if (ok) {
// 加载 /WEB-INF/classes/META-INF/resources 目录下资源
resourcesStart();
}
// 设置加载器
if (getLoader() == null) {
WebappLoader webappLoader = new WebappLoader();
webappLoader.setDelegate(getDelegate());
setLoader(webappLoader);
}
// An explicit cookie processor hasn't been specified; use the default
// cookie 处理器
if (cookieProcessor == null) {
cookieProcessor = new Rfc6265CookieProcessor();
}
// Initialize character set mapper
// 初始化 CharsetMapper
getCharsetMapper();
// Validate required extensions
// 验证 /META-INF/MANIFEST.MF
boolean dependencyCheck = true;
try {
dependencyCheck = ExtensionValidator.validateApplication
(getResources(), this);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.extensionValidationError"), ioe);
dependencyCheck = false;
}
// 验证失败, application 不可用
if (!dependencyCheck) {
// do not make application available if dependency check fails
ok = false;
}
// Reading the "catalina.useNaming" environment variable
// catalina.useNaming 环境变量
String useNamingProperty = System.getProperty("catalina.useNaming");
if ((useNamingProperty != null)
&& (useNamingProperty.equals("false"))) {
useNaming = false;
}
if (ok && isUseNaming()) {
if (getNamingContextListener() == null) {
NamingContextListener ncl = new NamingContextListener();
ncl.setName(getNamingContextName());
ncl.setExceptionOnFailedWrite(getJndiExceptionOnFailedWrite());
// 注册 LifecycleListener
addLifecycleListener(ncl);
setNamingContextListener(ncl);
}
}
// Standard container startup
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Processing standard container startup");
// Binding thread
ClassLoader oldCCL = bindThread();
try {
if (ok) {
// Start our subordinate components, if any
Loader loader = getLoader();
if (loader instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) loader).start();
}
// since the loader just started, the webapp classloader is now
// created.
setClassLoaderProperty("clearReferencesRmiTargets",
getClearReferencesRmiTargets());
setClassLoaderProperty("clearReferencesStopThreads",
getClearReferencesStopThreads());
setClassLoaderProperty("clearReferencesStopTimerThreads",
getClearReferencesStopTimerThreads());
setClassLoaderProperty("clearReferencesHttpClientKeepAliveThread",
getClearReferencesHttpClientKeepAliveThread());
setClassLoaderProperty("clearReferencesObjectStreamClassCaches",
getClearReferencesObjectStreamClassCaches());
setClassLoaderProperty("clearReferencesThreadLocals",
getClearReferencesThreadLocals());
// By calling unbindThread and bindThread in a row, we setup the
// current Thread CCL to be the webapp classloader
unbindThread(oldCCL);
oldCCL = bindThread();
// Initialize logger again. Other components might have used it
// too early, so it should be reset.
logger = null;
getLogger();
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if(null != realm) {
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
}
// Place the CredentialHandler into the ServletContext so
// applications can have access to it. Wrap it in a "safe"
// handler so application's can't modify it.
CredentialHandler safeHandler = new CredentialHandler() {
@Override
public boolean matches(String inputCredentials, String storedCredentials) {
return getRealmInternal().getCredentialHandler().matches(inputCredentials, storedCredentials);
}
@Override
public String mutate(String inputCredentials) {
return getRealmInternal().getCredentialHandler().mutate(inputCredentials);
}
};
context.setAttribute(Globals.CREDENTIAL_HANDLER, safeHandler);
}
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
// 调用事件
fireLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
// Start our child containers, if not already started
// 在不可用的时候,启动子容器
for (Container child : findChildren()) {
if (!child.getState().isAvailable()) {
child.start();
}
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic),
// if any
// pipeline 的启动
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
// Acquire clustered manager
// 获取集群管理器
Manager contextManager = null;
Manager manager = getManager();
if (manager == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardContext.cluster.noManager",
Boolean.valueOf((getCluster() != null)),
Boolean.valueOf(distributable)));
}
if ((getCluster() != null) && distributable) {
try {
contextManager = getCluster().createManager(getName());
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("standardContext.clusterFail", ex);
ok = false;
}
} else {
contextManager = new StandardManager();
}
}
// Configure default manager if none was specified
// 配置默认管理器
if (contextManager != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardContext.manager",
contextManager.getClass().getName()));
}
setManager(contextManager);
}
// 注册管理器
if (manager!=null && (getCluster() != null) && distributable) {
//let the cluster know that there is a context that is distributable
//and that it has its own manager
getCluster().registerManager(manager);
}
}
if (!getConfigured()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.configurationFail"));
ok = false;
}
// We put the resources into the servlet context
// 将资源 放到 servlet Context 中
if (ok) {
getServletContext().setAttribute
(Globals.RESOURCES_ATTR, getResources());
if (getInstanceManager() == null) {
javax.naming.Context context = null;
if (isUseNaming() && getNamingContextListener() != null) {
context = getNamingContextListener().getEnvContext();
}
Map<String, Map<String, String>> injectionMap = buildInjectionMap(
getIgnoreAnnotations() ? new NamingResourcesImpl(): getNamingResources());
setInstanceManager(new DefaultInstanceManager(context,
injectionMap, this, this.getClass().getClassLoader()));
}
getServletContext().setAttribute(
InstanceManager.class.getName(), getInstanceManager());
InstanceManagerBindings.bind(getLoader().getClassLoader(), getInstanceManager());
// Create context attributes that will be required
getServletContext().setAttribute(
JarScanner.class.getName(), getJarScanner());
// Make the version info available
getServletContext().setAttribute(Globals.WEBAPP_VERSION, getWebappVersion());
}
// Set up the context init params
// 设置上下文 init 参数
mergeParameters();
// Call ServletContainerInitializers
for (Map.Entry<ServletContainerInitializer, Set<Class<?>>> entry :
initializers.entrySet()) {
try {
entry.getKey().onStartup(entry.getValue(),
getServletContext());
} catch (ServletException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.sciFail"), e);
ok = false;
break;
}
}
// Configure and call application event listeners
// 调用 listener
if (ok) {
if (!listenerStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.listenerFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Check constraints for uncovered HTTP methods
// Needs to be after SCIs and listeners as they may programmatically
// change constraints
if (ok) {
checkConstraintsForUncoveredMethods(findConstraints());
}
try {
// Start manager
Manager manager = getManager();
if (manager instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) manager).start();
}
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.managerFail"), e);
ok = false;
}
// Configure and call application filters
// filter调用
if (ok) {
if (!filterStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.filterFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Load and initialize all "load on startup" servlets
// 初始化 Servlet,如果配置了 LoadOnStartUp
if (ok) {
if (!loadOnStartup(findChildren())){
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.servletFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Start ContainerBackgroundProcessor thread
// 启动后台线程
super.threadStart();
} finally {
// Unbinding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
}
// Set available status depending upon startup success
if (ok) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled())
log.debug("Starting completed");
} else {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.startFailed", getName()));
}
startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
// Send j2ee.state.running notification
if (ok && (this.getObjectName() != null)) {
Notification notification =
new Notification("j2ee.state.running", this.getObjectName(),
sequenceNumber.getAndIncrement());
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
// The WebResources implementation caches references to JAR files. On
// some platforms these references may lock the JAR files. Since web
// application start is likely to have read from lots of JARs, trigger
// a clean-up now.
// 资源回收
getResources().gc();
// Reinitializing if something went wrong
if (!ok) {
setState(LifecycleState.FAILED);
} else {
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}
}StandardWrapper
构造方法
public StandardWrapper() {
super();
swValve=new StandardWrapperValve();
// 设置 BasicValve
pipeline.setBasic(swValve);
broadcaster = new NotificationBroadcasterSupport();
}startInternal
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Send j2ee.state.starting notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.state.starting",
this.getObjectName(),
sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
// Start up this component
super.startInternal();
setAvailable(0L);
// Send j2ee.state.running notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification =
new Notification("j2ee.state.running", this.getObjectName(),
sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
}StandardPipeline
initInternal
@Override
protected void initInternal() {
// NOOP
}startInternal
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
Valve current = first;
if (current == null) {
current = basic;
}
while (current != null) {
if (current instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) current).start();
current = current.getNext();
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}









